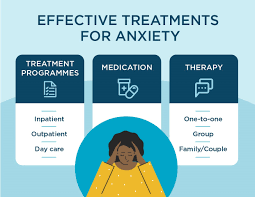
Anxiety Treatment. Anxiety disorders are often treated with a combination of psychotherapy and medications. The most effective form of psychotherapy is cognitive behavioral therapy. (CBT), which can help people learn to think, react, and behave differently to feel less to think, react anxious. Medications can help relieve symptoms, but they would cure anxiety disorder.
Anxiety Treatment: An Overview
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of worry, fear, or nervousness, which can interfere with daily life and well-being. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available for managing and reducing anxiety. These treatments can be used individually or in combination, depending on the severity and type of anxiety.
1. Psychological Therapies (Psychotherapy)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- What It Is: CBT is one of the most effective and commonly used therapies for anxiety. It focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety and replacing them with more balanced, realistic thoughts.
- How It Helps: By changing unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, CBT helps individuals develop coping strategies and better manage anxious feelings.
- Duration: CBT typically involves a series of sessions (often 12-20), although it can vary depending on the individual.
Exposure Therapy
- What It Is: Exposure therapy is a type of CBT that involves gradual exposure to the situations or objects that cause anxiety, with the goal of desensitizing the person to those triggers.
- How It Helps: Over time, repeated exposure helps reduce the fear response and allows the individual to handle anxiety-provoking situations more comfortably.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
- What It Is: DBT is a form of therapy that helps individuals manage emotions, reduce self-destructive behaviors, and improve relationships. It combines aspects of cognitive-behavioral therapy with mindfulness and acceptance techniques.
- How It Helps: DBT can help those with anxiety disorders manage intense emotions and develop skills to cope with stress and anxiety in healthy ways.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
- What It Is: ACT encourages individuals to accept their thoughts and feelings instead of trying to control or eliminate them. The therapy emphasizes mindfulness and living in accordance with one’s values.
- How It Helps: By accepting anxiety as a natural experience, individuals can learn to act in ways that align with their values, despite their anxious feelings.
2. Medications for Anxiety
Antidepressants (SSRIs and SNRIs)
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Medications like fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and escitalopram (Lexapro) are commonly prescribed for anxiety disorders. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which helps regulate mood and anxiety.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Medications like venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) target both serotonin and norepinephrine to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Benzodiazepines
- What They Are: Medications like lorazepam (Ativan), diazepam (Valium), and alprazolam (Xanax) are fast-acting drugs used for short-term relief of anxiety symptoms.
- How They Help: Benzodiazepines work by calming the nervous system and reducing feelings of anxiety. However, due to their potential for dependence and addiction, they are typically prescribed for short-term use only.
Beta-Blockers
- What They Are: Medications like propranolol (Inderal) are sometimes prescribed for anxiety, particularly for physical symptoms like rapid heart rate or tremors that accompany anxiety.
- How They Help: Beta-blockers block the effects of adrenaline, helping to control physical symptoms associated with anxiety. They are often used for performance anxiety (e.g., stage fright).
Buspirone
- What It Is: Buspirone (Buspar) is an anti-anxiety medication that is often used for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
- How It Helps: Unlike benzodiazepines, buspirone has a lower risk of dependency and is typically used for long-term management of anxiety.
3. Lifestyle Changes and Self-Help Strategies
Mindfulness Meditation
- What It Is: Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment and observing thoughts and feelings without judgment. Meditation practices can help individuals learn to manage anxiety by fostering awareness and acceptance.
- How It Helps: Mindfulness meditation reduces stress and enhances emotional regulation, which can significantly reduce anxiety levels.
Exercise
- What It Is: Physical activity, such as walking, running, or yoga, can have a profound impact on mental healthhttps://www.scripps.org/news_items/4783-how-to-choose-over-the-counter-pain-medicine.
- How It Helps: Regular exercise releases endorphins (feel-good chemicals in the brain), reduces stress hormones, and can help regulate mood, making it a natural and effective anxiety treatment.
Breathing Techniques
- What It Is: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing, can help manage anxiety in the moment.
- How It Helps: Controlled breathing can help calm the nervous system, reduce physical tension, and promote a feeling of relaxation, making it easier to manage anxiety symptoms.
Sleep Hygiene
- What It Is: Practicing good sleep habits is important for managing anxiety.
- How It Helps: Poor sleep can exacerbate anxiety, so focusing on regular sleep patterns, avoiding caffeine late in the day, and creating a calming bedtime routine can improve anxiety symptoms.
Social Support
- What It Is: Talking to friends, family, or a support group can help individuals manage their anxiety.
- How It Helps: Social support provides emotional validation, reduces feelings of isolation, and helps individuals feel more connected, all of which can help reduce anxiety.
4. Alternative Treatments
Herbal Supplements
- What They Are: Some people find relief from anxiety through natural supplements like chamomile, valerian root, lavender, or passionflower.
- How They Help: While these supplements may have calming effects, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before using them, especially if you are already taking prescribed medication.
Acupuncture
- What It Is: Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- How It Helps: Acupuncture may help reduce stress and anxiety by promoting relaxation and balancing the body’s energy (qi).
Aromatherapy
- What It Is: Essential oils, such as lavender, rose, or sandalwood, are used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation.
- How It Helps: Aromatherapy can help calm the mind and body and reduce symptoms of anxiety.
5. When to Seek Professional Help
- Persistent Anxiety: If anxiety is affecting your daily life, work, or relationships, it may be time to seek help from a mental health professional.
- Co-occurring Conditions: If anxiety is accompanied by depression, panic attacks, or substance abuse, treatment may involve a combination of therapy and medication.
- Increased Symptoms: If anxiety symptoms worsen, or if they lead to thoughts of self-harm or suicide, it is important to seek immediate help from a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a treatable condition, and there are various options available to help manage and alleviate symptoms. Whether you prefer therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of approaches, it’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to find the most effective treatment plan for your needs. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life despite anxiety.